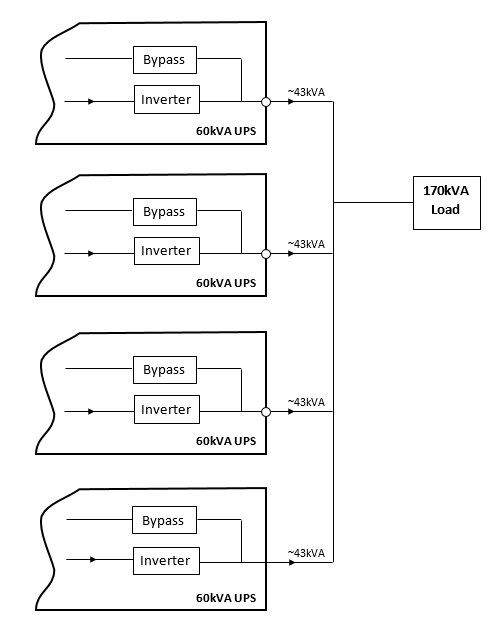
| System Redundancy In a Redundant Parallel System, the number of UPS that make up the Parallel System is at least one device greater than the number required by the system’s main capacity. |
| For example, the following figure shows 4 UPS 60kVA used to supply 170kVA. Thus, if one of the UPS fails, the system can still supply the load energy by the inverter energy, thereby increasing the reliability of the system.
In the example above, all four UPSs in the system work in redundant mode, if one of the devices crashes, the load will still use the energy generated by the inverter and will automatically switch to the second UPS only after the second UPS crashes. The bypass route is passed. If you need a more secure power source, the number of redundant units (UPSs) can be doubled (or more if you need an ultra-reliable power supply). For this reason this type of system is sometimes referred to as ‘N + 1’ or ‘N + 2’, where N represents the minimum number of UPS needed and 1 or 2 numbers and so on. Specifies reservation systems.
|