| Parallel systems The system consists of two or more UPSs that supply the same amount of electricity as a single load group and are generally applicable to on-line systems with a medium or high power range. |
| The units that make up such an extensive system often have the same functionality because they work together as they work individually. In fact, some manufacturers design their own UPSs so that they can be used in any situation without the need for complex modifications.
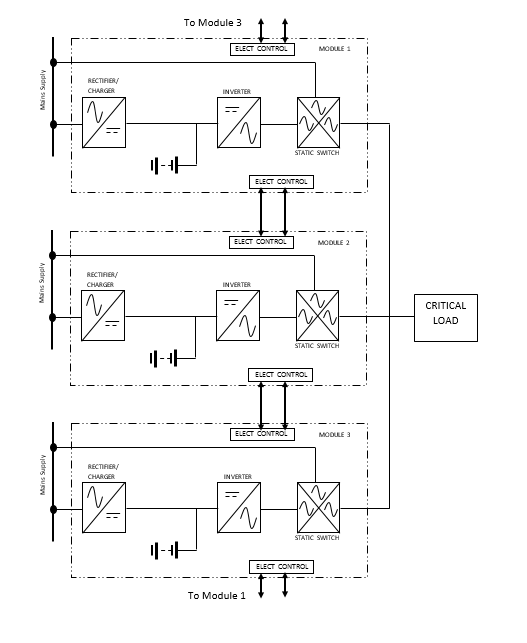
The following diagram shows a block diagram for three types of parallel systems.
Each section contains a static switch to allow for the transfer of load between the inverter and the bypass path. However, precision electronic control boards are installed within the system to ensure that all static switches operate simultaneously when moving from one power source (such as inverter UPS) to another (bypass path). Otherwise, the system would be in trouble if all the UPS used their inverter to transfer an output UPS to the bypass path. Also, more complete control circuits are needed to divide the load between the inverters and their synchronization. The control commands are transmitted through low-voltage circuits through the cables with circular connectors, allowing each segment to communicate with other parts of the system. One of the benefits of complete isolation of inputs and outputs in each segment is that each UPS is completely isolated from other parts and can be used without the need for other UPSs. Removed the comment from the system. There are two main reasons for installing a parallel system, firstly, that the effective power and capacity of the UPS are high enough to enable the system to supply the energy required for high power loads, whereas a single UPS cannot. To provide. The second reason is the increase in the number of devices to increase the reliability of the system. Parallel UPSs can usually be categorized into one of the Capacity or Redundancy systems, although some of them are sufficiently capable of responding to both performance depending on what the whole system is going to do. Show. Regardless of the UPS model selected, all UPSs that form part of a parallel system must be of the same type and have the same output power. In other words, a single 30kVA UPS cannot be Paralleled 120kVA.
|